Inner Health? The 4 Vital Functions of the Gut
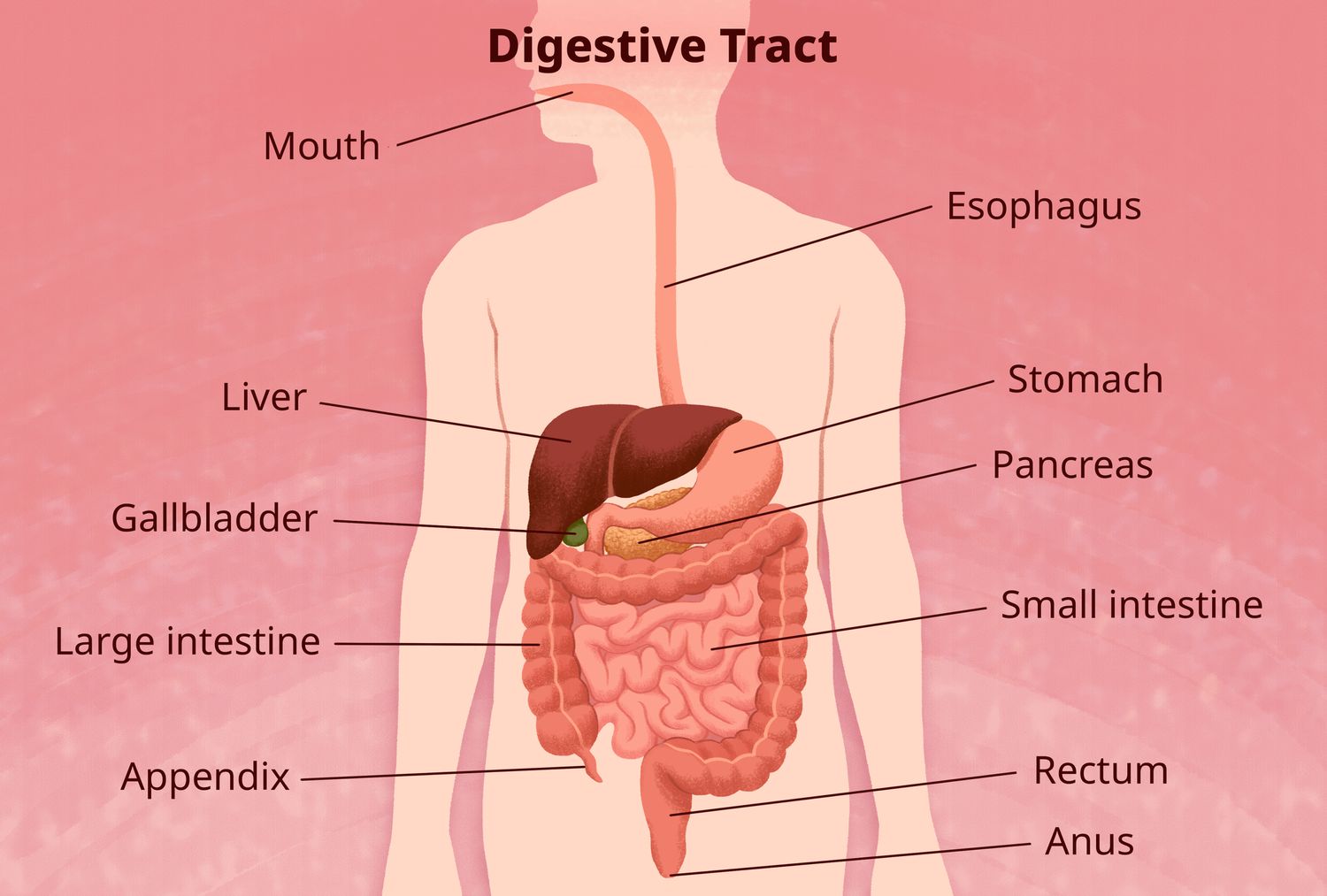
Have you ever wondered about the incredible capabilities of your digestive system? The gastrointestinal tract, often referred to as the gut, is a complex network of organs and tissues responsible for a wide range of vital functions. From the breakdown and absorption of nutrients to immune defense and even its surprising connection with the brain, the gut plays a remarkable role in maintaining our overall health. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of the gastrointestinal tract and shed light on its normal functions.
Digestion and Absorption:
One of the primary functions of the gastrointestinal tract is to break down food into smaller, more manageable components. Through the combined efforts of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine, food is mechanically and chemically processed into nutrients and fluids. Enzymes and stomach acid work together to break down complex molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into simpler forms that can be easily absorbed.
Once the food is sufficiently broken down, the small intestine takes center stage in absorption. Here, the nutrients and fluids are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to various parts of the body to provide energy and support overall bodily functions. The efficiency of this process ensures that the body receives the necessary nourishment to thrive.
Immune Defense:
Did you know that a significant portion of your immune system resides in your gut? Approximately 70-80% of the body’s immune cells are located within the gastrointestinal tract, emphasizing its crucial role in immune defense. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a network of immune cells and tissues that act as a first line of defense against harmful pathogens.
The GALT plays a pivotal role in distinguishing between harmful bacteria and beneficial microorganisms present in the gut. It helps maintain a delicate balance, ensuring the protection of the body while fostering a harmonious relationship with the trillions of beneficial bacteria in our intestines.
Brain-Gut Axis:
The gut has a fascinating connection with the nervous system, leading to its nickname as the “second brain.” The brain-gut axis represents the two-way communication between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system. This complex network involves a constant exchange of information, signaling, and coordination.
The gut produces an array of neurotransmitters and hormones that transmit signals to the brain, influencing mood, behavior, and even cognitive function. Similarly, the brain sends signals to the gut, affecting its motility, secretions, and overall function. This intricate connection highlights the significant impact the gut can have on our mental well-being.
House of the Intestinal Microbiome:
Within the gut, an ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the intestinal microbiome, thrives. This diverse community of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of the gastrointestinal tract. The microbiome aids in digestion, produces essential vitamins, helps regulate the immune system, and even influences brain function.
Imbalances in the intestinal microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various gastrointestinal disorders and even impact overall health. Nurturing a healthy microbiome through a balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics can contribute to optimal gut function and overall well-being.
Conclusion:
The gastrointestinal tract is a remarkable system that encompasses the processes of digestion, absorption, immune defense, brain-gut axis interactions, and the dynamic world of the intestinal microbiome. By understanding and appreciating the normal functions of our gut, we can make informed choices to support its well-being and maintain optimal health. Nurturing our gastrointestinal health through a wholesome diet, regular physical activity, and mindful lifestyle choices will undoubtedly pave the way for a healthier and happier life.